Debugging Client Scripts
There are several strategies for debugging client-side scripts:
- JavaScript Log and jslog()
- Field Watcher
- try/catch
- Debugging tools built into web browsers (browser dependent)
JavaScript Log and jslog()
Client-side scripts can use the jslog() method to write messages to the JavaScript log. Pass the jslog() method to the information you want to appear in the message:
- Strings
- g_form methods
- g_user properties and methods
- Variables
JavaScript string escape characters such as \n (newline) and \t (tab) will not cause errors in the jslog() method but are ignored.
function onLoad(){
var myVar = 3;
jslog("This message is from jslog().");
jslog("The value of myVar = " + myVar);
jslog("The Priority value = " + g_form.getValue('priority'));
jslog("The first name of the currently logged in user is " + g_user.firstName + ".");
}
To view the output from the jslog() method, use the JavaScript Log.
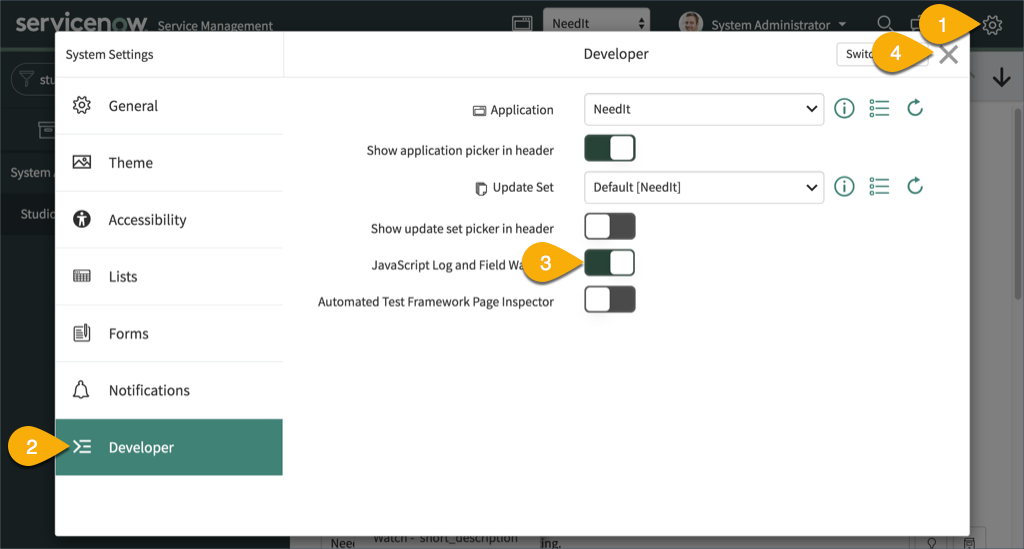
- In the main ServiceNow browser window, click the Settings button.
- Open the Developer pane.
- Enable the JavaScript Log and Field Watcher.
- Close the System Settings dialog.
5. The JavaScript Log opens in a new pane at the bottom of the main ServiceNow browser window.
6. The jslog() output appears in the JavaScript Log.
The JavaScript Log is accessible only by users with the admin role and is session-based. Opening the JavaScript Log does not impact other users.
DEVELOPER TIP: To make it easy to locate error messages, consider adding your initials or some other identifying string to the start of each of your log messages:
jslog("ME: The value of myVar = " + myVar);
try/catch
ServiceNow’s Script Editor provides syntax checking (unpaired “, missing ; and other syntax issues) and cannot find runtime issues such as bad function calls. To find information for runtime problems, use JavaScript’s try/catch statement. In the example script, the function helloWorld() is not defined. Although the script does not have syntax errors, it throws a runtime error.
function onLoad() {
// Using Try/Catch to trap runtime errors.
// The helloWorld() function does not exist.
try{
helloWorld();
}
catch(err){
jslog('A JavaScript runtime error occurred: ' + err.message);
}
}
The JavaScript err object has two useful properties:
The example script displays err.message.
To catch custom errors, use the JavaScript throw() method.
Browser Debuggers
For debugging client-side scripts, many developers use console.log() to write information to browser debuggers. Although this strategy is allowed, it is not required because the jslog() method also writes to browser debuggers. Opening and using browser-based debuggers is not covered in this module. The example script writes debugging messages using both the jslog() and console.log() methods.
function onLoad() {
jslog("This message was written by the jslog() method.");
console.log("This message was written by console.log().");
}
Both the jslog() and console.log() messages appear in the browser’s debugger.
https://medium.com/@LearnITbyPrashant/debugging-client-scripts-2c3660158864?source=rss-d005fc598f0a------2